If your Chevy’s check engine light is on and you’re seeing a “Transmission Control System MIL Request,” it might seem like a huge problem. Don’t worry, lots of people face this. It can be tricky, but it’s often something you can tackle. We’ll explore How to Fix Transmission Control System MIL Request on Chevy step by step, making it easy to follow. Get ready to learn about the most common causes and simple fixes. Let’s begin.
Decoding the Check Engine Light and the Transmission
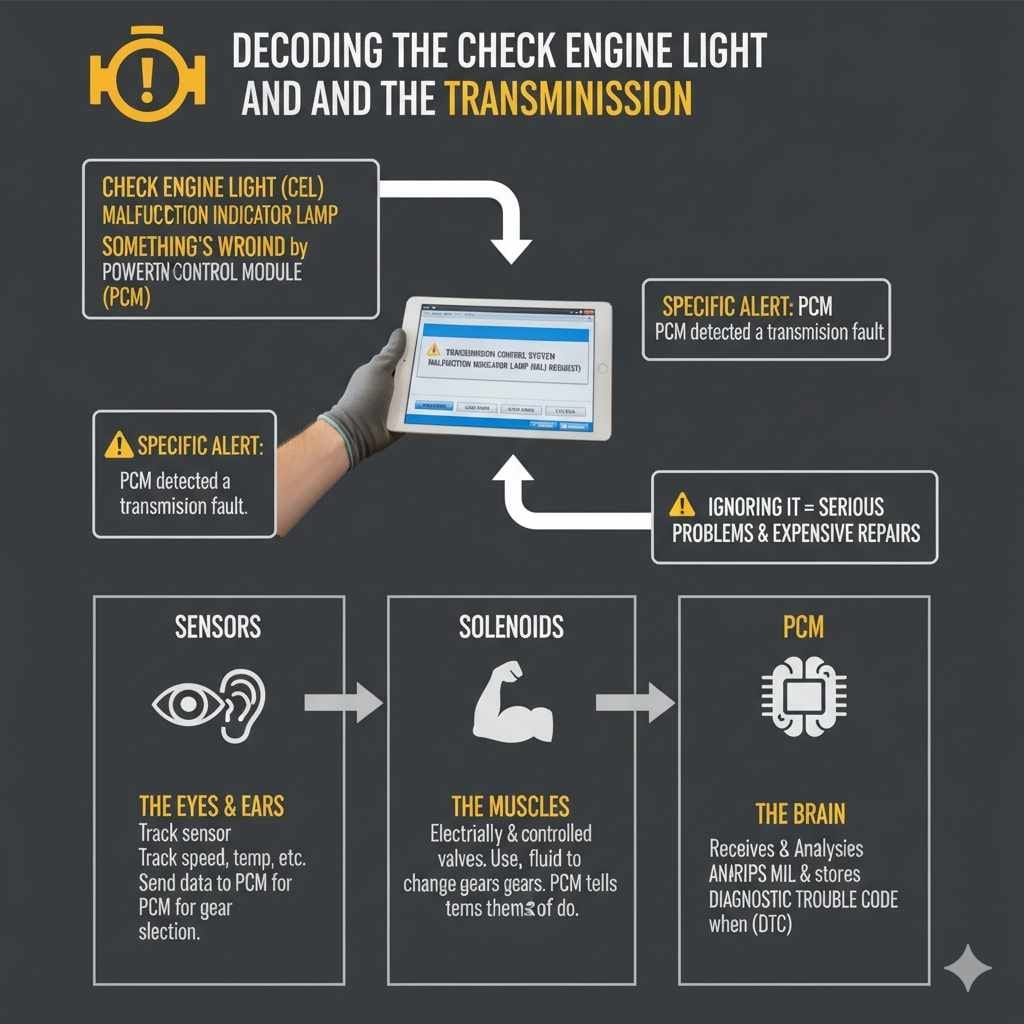
The check engine light (CEL), also known as the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), is your car’s way of telling you something’s wrong. It’s connected to the car’s computer, the powertrain control module (PCM), which monitors everything. The “Transmission Control System MIL Request” message is a specific alert, meaning the PCM has detected a problem with how the transmission is working. This is usually due to a fault within the transmission system itself, triggering the light to illuminate on your dashboard. Ignoring it can lead to more serious problems down the line, affecting your car’s performance and potentially causing expensive repairs.
What the Transmission Control System Actually Does
The transmission control system is a crucial part of your car, responsible for smoothly changing gears. It ensures your car gets the correct power and speed without overworking the engine. It’s essentially the brain of your car’s gearbox. Without it, you’d have to manually shift gears, something many modern vehicles no longer accommodate. The system uses sensors, solenoids, and the PCM to manage gear changes and overall transmission behavior. All these components must work together in order for it to function correctly.
-
- Sensors: These devices track various aspects of the transmission’s performance. They can monitor the speed of the input shaft, output shaft, transmission fluid temperature, and more.
Sensors are like the eyes and ears of your transmission control system. They send information to the PCM about the current state of the transmission. The information provided by these sensors are essential for the proper gear selections and overall operation of the transmission.
-
- Solenoids: These are electrically controlled valves that regulate the flow of transmission fluid. This is what actually changes the gears.
Solenoids are the muscles of the transmission control system. They receive electrical signals from the PCM and use them to direct hydraulic pressure within the transmission. This movement allows the gears to shift. If the solenoids fail, gear changes can become erratic or fail completely.
-
- Powertrain Control Module (PCM): The PCM is the central computer that controls the transmission. It receives information from the sensors and uses it to operate the solenoids.
The PCM is the brain of the operation. It receives input from the sensors, analyzes the data, and then sends instructions to the solenoids. It makes real-time adjustments to your transmission’s operation. When the PCM detects a fault, it triggers the MIL and stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
Common Causes of a Transmission Warning
Several issues can cause the “Transmission Control System MIL Request” to appear. These can range from minor problems to more serious ones. Because of the vastness of the problem, it helps to understand what the most common issues are. Identifying these problems early will save you time and money. Knowing them can also prevent further damage.
-
- Low Transmission Fluid: If your transmission fluid is too low, it can lead to problems. This can cause the transmission to overheat or malfunction.
Transmission fluid is essential for lubricating and cooling the transmission’s internal components. A leak, or simply neglecting to maintain the proper fluid level, can lead to serious damage. Regularly checking your fluid level and performing fluid changes is one of the best ways to extend the life of your transmission. A low level will certainly trigger the MIL.
-
- Faulty Sensors: As mentioned earlier, sensors provide important data to the PCM. A bad sensor can give inaccurate readings, causing the system to misbehave.
Sensors can fail due to wear, electrical issues, or contamination. A failed sensor will provide an incorrect output that could cause the transmission to shift at incorrect times. They could also have other negative impacts on performance. Replacement of faulty sensors is a fairly common solution.
-
- Solenoid Problems: Solenoids can get stuck, fail, or otherwise not function correctly, leading to shifting problems.
Solenoids are critical for gear changes. Problems with solenoids usually result in erratic shifting, hard shifts, or a complete failure to shift. These are usually electrical problems and can range from a bad connection to a damaged solenoid.
-
- Software Issues or PCM Faults: Sometimes, the problem lies within the car’s computer itself.
The PCM controls all aspects of the transmission, and any fault will cause the MIL. Software glitches, power surges, or physical damage can lead to problems. In these situations, your vehicle will trigger the MIL and likely provide a code as well.
Diagnosing the Problem and Clearing the Codes
Figuring out what’s causing the “Transmission Control System MIL Request” is the first step. You’ll need some tools and some know-how to get started. Don’t worry, it’s possible for anyone to perform the steps themselves. This process will identify the root cause so you can address it and get your Chevy back on the road. Remember, diagnosing problems early is very important.
Using a Diagnostic Tool
A diagnostic tool, also known as a code reader or scanner, is the best starting point. These devices connect to your car’s OBD-II port (usually under the dashboard) and can read the trouble codes stored in the PCM. These codes provide clues about what’s going wrong. They will give you a place to begin the diagnosis. You will want to write down the code for future reference.
-
- OBD-II Port: This is the standardized port where you plug in the scanner. It’s usually located below the steering wheel, on the driver’s side.
Most vehicles made after 1996 have an OBD-II port. This makes it easy to connect and retrieve the information from the car’s computer. The port provides a standard interface.
-
- Code Reader: A basic code reader will display the trouble codes, such as P0700, which is a generic transmission control system code.
Code readers are relatively inexpensive and can provide you with the most basic information. They usually provide the code and a description of what it means.
-
- Advanced Scanner: An advanced scanner can provide much more information, including live data, which shows how various sensors are performing.
Advanced scanners can allow you to view data such as transmission fluid temperature, and solenoid operation. They can also help with more advanced diagnostics.
Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Once you have a code, you’ll need to understand what it means. The code’s meaning can guide you toward the area of the issue. You can use online resources such as the internet to look up the code. Each code has a specific meaning, telling you which part of the system is having a problem. Some common transmission codes, like P0700, are generic codes. Others are more specific, pointing to a particular sensor or solenoid. Understanding the code will help you determine the next steps.
-
- Code Formats: Codes typically follow a format like P0700, where ‘P’ indicates a powertrain code.
The first digit specifies the area of the vehicle the problem is related to. The remaining digits give a more specific description. Understanding these formats will help you to pinpoint the origin of the problem.
-
- Common Transmission Codes: Codes like P0700 (Transmission Control System Malfunction), P0741 (Torque Converter Clutch Performance), and P0711 (Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor A Circuit Range/Performance) are very common.
These codes offer a starting point for the diagnostic process. Each one points to an area for investigation. Identifying the correct DTC can help to begin the troubleshooting process.
-
- Researching Codes: Use online resources, repair manuals, or professional tools to understand what each code means.
You can get detailed information on potential causes, troubleshooting steps, and possible solutions by researching codes. Many websites offer free resources for code identification.
Clearing the Codes
After you’ve identified and fixed the issue, you’ll need to clear the codes from the PCM. This removes the check engine light and allows you to confirm that the repair has been successful. Using a code reader is an easy way to clear codes. You can also drive your car for a while, as the PCM often clears codes automatically if the problem is fixed.
-
- Code Reader Function: Most code readers have a “clear codes” or “erase codes” function.
This will reset the PCM and remove the codes that were stored. Follow the code reader’s instructions to perform this action.
-
- Test Drive: After clearing the codes, take your car for a test drive. If the light doesn’t come back on, the problem is likely fixed.
Driving will allow the PCM to re-run the diagnostics and confirm that there are no remaining issues. This helps to check the validity of the fix you did.
-
- Re-scanning: If the check engine light returns, rescan the car to see if the same or new codes have reappeared.
If the light comes back on, it means the problem wasn’t fully resolved. You’ll need to further investigate and address the underlying cause. Rescanning will help to see the results of the repair.
Common Repairs and Maintenance
Once you’ve diagnosed the problem, you can start the repairs. It is important to know that some repairs are fairly straightforward, while others require more skills or professional help. The goal is to address the issue and restore your Chevy’s transmission to its optimal state. Performing regular maintenance can help keep your transmission operating at its best. Taking the right steps can prevent more serious, expensive repairs down the road.
Transmission Fluid and Filter Replacement
Regular transmission fluid changes are essential. Transmission fluid lubricates, cools, and cleans the transmission. The filter removes debris and contaminants. Changing the fluid and filter ensures that your transmission remains healthy. This will help to prevent many problems from arising. If the fluid is dirty or low, it will trigger the MIL and you will need to get it replaced.
-
- Frequency: Change the fluid and filter based on your Chevy’s recommendations. Usually, this is every 30,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the car model and how you drive.
Following the manufacturer’s recommendations is a great way to extend the life of your transmission. This helps to make sure that the system is properly maintained.
-
- Process: This often involves draining the old fluid, removing the transmission pan, replacing the filter, and refilling with new fluid.
You can usually do this at home. Many tutorials are available online. Make sure you use the proper fluid type, as specified in your owner’s manual.
-
- Fluid Type: Use the correct type of transmission fluid for your Chevy model. Incorrect fluid can damage the transmission.
Check your owner’s manual to find the correct fluid type. Using the wrong fluid can cause serious damage and trigger the MIL.
Sensor Replacement
If a faulty sensor is the issue, replacing it is often a simple fix. Sensors are often easily accessible. You can often buy them at an auto parts store. Make sure you get the correct part for your Chevy model. Replace a sensor using the instructions for your vehicle. Then clear the codes and take a test drive to confirm the repair.
-
- Locating Sensors: Refer to your service manual or online resources to find the sensor’s location.
This makes the repair easier and faster. The exact location will vary depending on the model and year.
-
- Replacement: Unplug the sensor, remove it, install the new sensor, and plug it back in.
This is usually a simple process. Make sure you disconnect the battery before working with electrical components.
-
- Test: After replacing the sensor, clear the codes and take the car for a test drive to check the result.
Make sure to verify that the check engine light does not come back on and that the transmission functions correctly. Scanning the vehicle again to confirm can ensure the issue is completely resolved.
Solenoid Replacement
Replacing solenoids can be more complicated than replacing sensors, but it can still be done at home. You’ll need to access the transmission pan. This might involve removing the transmission pan. Then, you’ll need to disconnect the electrical connector, remove the solenoid, and install the new one. Make sure you follow the service manual. After that, install a new transmission fluid and clear the codes.
-
- Accessibility: The solenoid location varies based on the vehicle, but is often found within the transmission.
Be prepared to work in a cramped space. You may need to remove parts to access the transmission. Consult the service manual for assistance with this part.
-
- Electrical Connections: Make sure to disconnect the electrical connector before removing the old solenoid.
This is essential for safety and to prevent electrical damage. Make sure you install the new solenoid properly.
-
- Torque Settings: When installing the new solenoid and reassembling components, follow the recommended torque settings to avoid damage.
Over-tightening or under-tightening can cause problems. Check the service manual for the proper settings.
Preventive Measures and Further Steps
Preventing future problems with your transmission is important. Regular maintenance, such as changing your fluids, can help. Paying attention to any unusual behavior can also help you to catch issues early. These measures will increase the life of your transmission and prevent bigger issues from arising. If the problem persists after these steps, it may be time to seek help from a professional.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Following a regular maintenance schedule is a great way to keep your Chevy running smoothly. This will reduce the likelihood of transmission problems. Stick to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Take care of your vehicle and it will take care of you.
-
- Fluid Changes: Change your transmission fluid and filter according to the recommended schedule.
Doing this will ensure the transmission has a steady supply of clean, lubricated fluid. This will reduce friction and wear.
-
- Check Fluid Levels: Make it a habit to regularly check the transmission fluid level. This is easily done.
Look for leaks or low levels, and address any issues quickly. Low levels can signal other problems are arising.
-
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the transmission for any signs of leaks, damage, or other issues.
Early detection can prevent more serious problems. Check the external components for any signs of issues.
When to Seek Professional Help
Sometimes, repairs go beyond what you can do at home. If you’ve tried the basics and the problem persists, it’s time to seek help from a professional. A mechanic will have the tools and experience to diagnose more complex issues. They can also perform repairs that require specialized equipment.
-
- Complex Issues: If you’re dealing with internal transmission problems, like a failed torque converter, seek help.
Internal issues can be complicated to diagnose and repair. These can also be costly, so you will want a professional.
-
- Advanced Diagnostics: Mechanics have access to advanced diagnostic equipment to provide deeper analysis.
A mechanic can run tests and get a better understanding of the issue. They can then identify the correct steps to repair it.
-
- Expertise: Mechanics have the expertise to make repairs and provide accurate estimates.
They can also give you insights into any other problems they find, such as future repairs. They also have the knowledge to fix these things correctly.

Additional Tips and Resources
For more detailed information, consult these resources. Repair manuals often have detailed troubleshooting steps. Online forums can also be very useful to learn about specific Chevy models. These tips will help you with more effective maintenance and problem-solving.
-
- Owner’s Manual: Your owner’s manual contains the specifications for your car and recommended maintenance schedules.
Consult your manual for specific information about your vehicle’s transmission fluid type, capacity, and other important details.
-
- Repair Manuals: Repair manuals, like those from Haynes or Chilton, provide step-by-step repair guides.
These manuals provide detailed information. You can use them to troubleshoot your vehicle.
-
- Online Forums: Online forums dedicated to Chevy models can be helpful for specific issues.
These forums provide advice and solutions from other owners. You can get help solving your problem.
Scenario 1: A Chevy owner notices the check engine light and a “Transmission Control System MIL Request” message. They use a code reader and find the code P0711 (Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor A Circuit Range/Performance). After some research, they determine that the sensor is likely faulty. They replace the sensor, clear the code, and the problem is resolved. The owner saves hundreds of dollars by doing the repair themselves.
Scenario 2: An owner notices rough shifting and the check engine light. They use a code reader to pull the P0741 code (Torque Converter Clutch Performance). They realize the issue is more than just a simple fix and seek help from a professional mechanic. The mechanic correctly diagnoses the problem and repairs the torque converter, and the car’s performance is restored.
| Issue | Possible Symptoms | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Low Transmission Fluid | Erratic shifting, slipping gears | Check and top off fluid; look for leaks |
| Faulty Sensor | Check engine light, inaccurate shifting | Use a code reader; replace faulty sensor |
| Solenoid Issues | Hard shifts, failure to shift | Check and replace solenoids |
| PCM Problems | Check engine light, various symptoms | Seek help from a professional |
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What does a “Transmission Control System MIL Request” mean?
Answer: It means your car’s computer has detected a problem with the transmission and triggered the check engine light.
Question: How do I find the OBD-II port in my Chevy?
Answer: The OBD-II port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the steering column.
Question: What does the P0700 code mean?
Answer: It means there is a general problem in the transmission control system.
Question: Should I drive my car if the check engine light is on?
Answer: It’s best to address the problem as soon as possible. Driving with a transmission issue can cause more damage.
Question: How often should I change my transmission fluid?
Answer: Follow the recommended schedule in your owner’s manual, often between 30,000 to 100,000 miles.
Final Thoughts
You now have a better grip on How to Fix Transmission Control System MIL Request on Chevy. It might seem complicated at first, but with a few tools and some knowledge, you can often address these issues. Remember to start by diagnosing the issue with a code reader, looking for the specific DTC, such as P0700 or P0741. From there, you can explore common fixes like fluid changes, sensor replacements, and solenoid repairs. Regular upkeep, like changing your transmission fluid and keeping an eye on your vehicle, is key to preventing problems. If you’re not comfortable working on your car, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. By staying informed and taking the correct steps, you can keep your Chevy running smoothly for years to come. Now you can get started fixing that transmission.

