Ever heard of the phrase, What Is Transmission Control Protocol in Computer Networks? It might sound tricky, but don’t worry! This can be a tough topic for many beginners because it involves some behind-the-scenes action of how the internet works. Think of it like learning how a car’s engine functions. This guide will break down this topic into simple steps, so you will totally get it. We’ll start with how data is sent across the internet, then we will explore what problems TCP solves, and more.
The Basics of Data Transfer
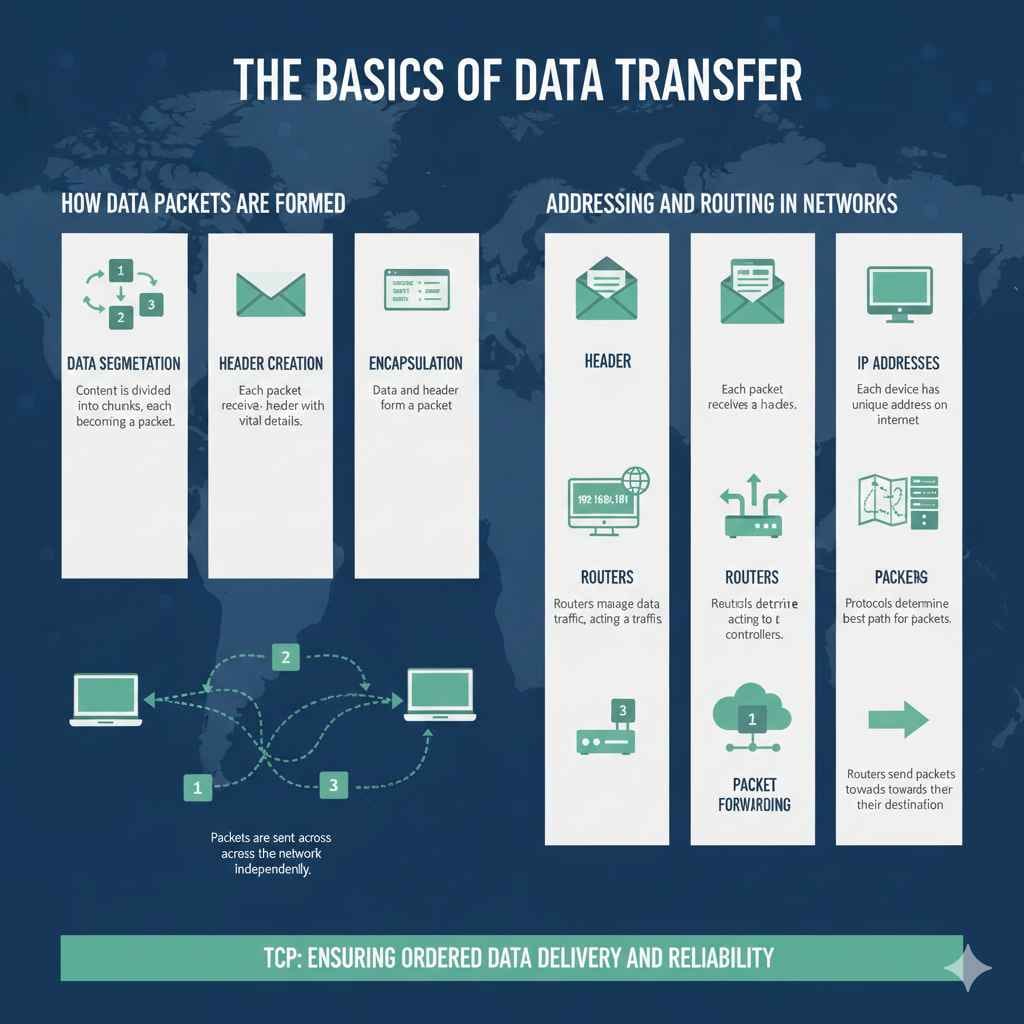
The internet is like a giant postal service for information. When you send an email, watch a video, or browse a website, data needs to travel from one computer to another. This data doesn’t just zoom across the network in one giant piece; it is broken up into smaller parts. Think of it like putting a big package into smaller boxes for easier shipping. Each of these small pieces of information is called a packet.
These packets need a way to find their way to the right place. Imagine sending letters without addresses! Each packet has a header. This header contains the destination address and other vital information. This helps ensure that the packets travel correctly.
How Data Packets Are Formed
Data packets are the building blocks of data transmission. They include all sorts of content, from a single character in an email to a huge video file that streams across a website. When a computer sends data, the data is sliced into these packets, each with a header that helps the network manage them.
- Data Segmentation: The content is divided into chunks, each becoming a packet. This helps with efficient transmission and error management.Imagine you’re sending a big book. It is easier to ship it in several boxes rather than one huge, heavy one. Data is the same way, divided to prevent any single packet from blocking up the network.
- Header Creation: Each packet receives a header, like a postal label.This header is packed with vital details. It contains the sender’s and receiver’s address, the sequence number (more on this later), and other important info that guides the packet to the destination.
- Encapsulation: The data and header combine.This is where the data and its address info are combined to form a packet, ready to be sent across the network. It’s like putting a letter (data) into an envelope (header).
- Transmission: Packets are sent across the network to their destination.These packets travel independently through the network. They could follow different routes to reach the same destination, like several trains running on different routes.
When you download something from the internet, your computer needs to figure out how to receive the incoming packets. If the data is not received correctly, it will ask for a resend. That is where TCP comes in. It helps arrange the packets so they make sense when they arrive at the other end. That’s because the packets do not always arrive in the same order.
Addressing and Routing in Networks
Packets need to be addressed correctly for everything to work. Every device on a network, like your computer, phone, or a server, has a unique address. This is the Internet Protocol (IP) address. This is similar to the address on a postal letter. Routing is the process of getting a packet from one place to another. Routers are like postal workers, using IP addresses to find the best route for packets to travel. Routers direct traffic across the internet to its destination. Without proper addressing and routing, data would never arrive at its destination.
- IP Addresses: Each device has a unique address.Think of it as the house address of your device on the internet. It helps the network identify where each packet needs to go.
- Routers: Routers manage data traffic.These are the traffic controllers of the internet. They examine the IP address on each packet and use this information to send the packets along the most efficient path to their destinations.
- Routing Protocols: Protocols like the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) help routers determine the best path.These protocols are like the roadmaps that routers use to make the best path decisions. They keep updating routes to avoid traffic jams and network failures.
- Packet Forwarding: Routers send packets from one network to another.Once a router selects the optimal route, it sends the packets on their way. This process continues until the packets arrive at their destination.
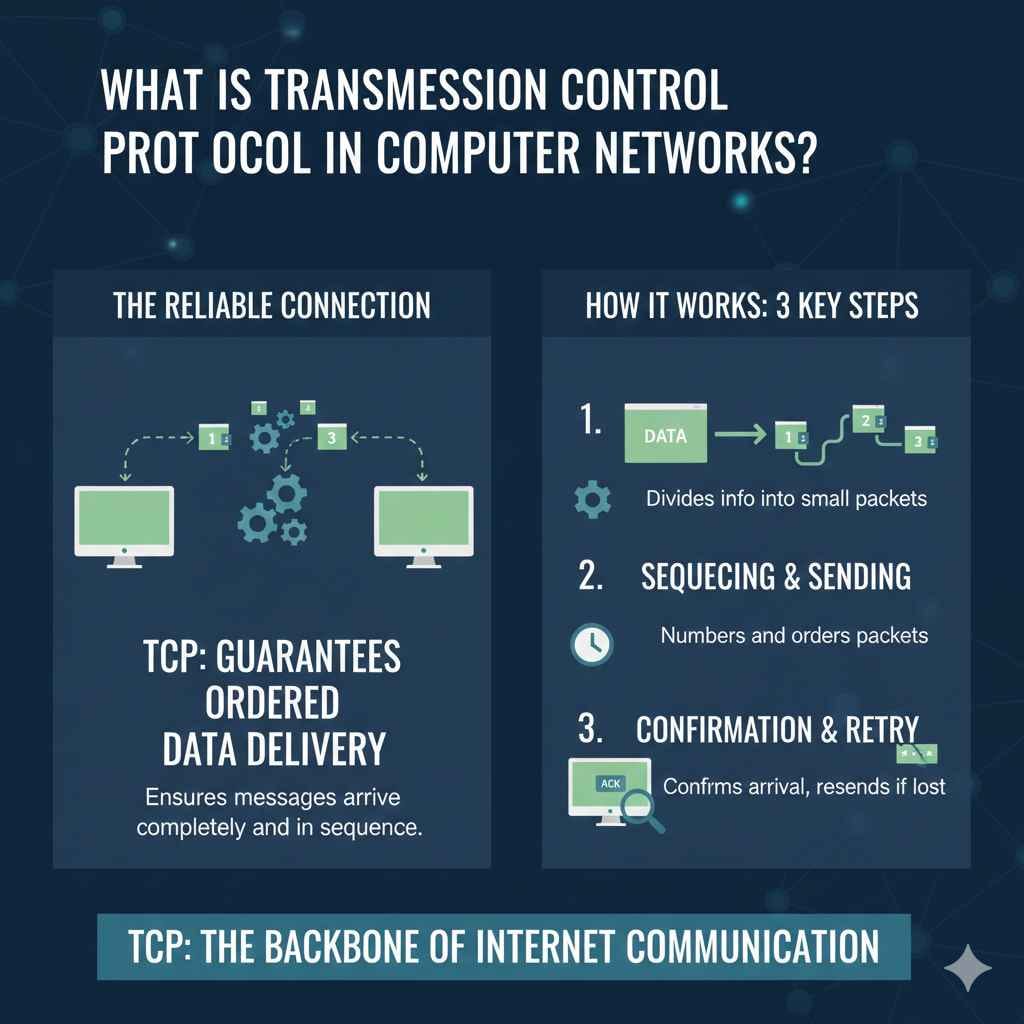
The Role of Transmission Control Protocol
What Is Transmission Control Protocol in Computer Networks? It is like the ultimate traffic controller for the internet. Its job is to ensure that data is delivered reliably. It’s the reason you can watch videos without any interruptions. Without TCP, all the data packets would be all over the place, like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle scattered on the floor. It manages connections, ensures data arrives in the correct order, and fixes any errors that may occur.
TCP’s main job is to provide reliable, ordered, and error-checked data transfer. It guarantees that the data sent is the same as the data received. This is done through a few main processes that make the internet so useful.
Key Features of TCP
TCP provides several features that help make the internet work smoothly. Here are some of the main functions.
- Connection-Oriented: TCP establishes a connection before data is sent.Before any data is transferred, TCP sets up a dedicated connection between the sender and the receiver. This is similar to a phone call. The connection is set up before the conversation begins.
- Reliable Data Transfer: It ensures that all data sent is received.TCP verifies that all data reaches its destination without errors. If any data is lost or damaged, it will be re-transmitted.
- Ordered Delivery: TCP ensures the data arrives in the correct order.Data is often sent in the form of multiple packets. TCP reassembles these packets in the correct order so the content makes sense. It is like putting the pages of a book back in order.
- Flow Control: TCP controls the rate of data transmission.Flow control prevents the sender from overwhelming the receiver with data. TCP adjusts the rate of transmission to match the receiver’s capacity to process the data.
When you download a file or stream a video, TCP guarantees that the data is sent completely. Imagine if a video was missing parts. That would be frustrating. TCP removes this problem.
How TCP Works: Step-by-Step
TCP uses a three-way handshake to set up a connection. This is the way it establishes, maintains, and tears down connections. Here’s a look at the process.
- Connection Establishment: The sender sends a SYN (synchronization) packet to the receiver.This is the first message to create a connection. The sender asks the receiver if it is ready to communicate.
- Synchronization and Acknowledgement: The receiver responds with a SYN-ACK (synchronization-acknowledgment) packet.The receiver acknowledges the request and sends a message back saying, “I am ready.”
- Confirmation: The sender replies with an ACK (acknowledgment) packet.The sender acknowledges that the receiver is ready, and the connection is established.
- Data Transfer: Data is then sent over the established connection.After the handshake, data can be sent reliably between the sender and the receiver. TCP ensures that all packets are received and acknowledges them.
- Connection Termination: The connection is closed after data transfer is completed.When communication is complete, the connection is closed. TCP uses a specific process to properly end the connection and free up network resources.
This handshake guarantees a solid connection that makes sure data transfers are successful. It’s like the pre-flight checks before an airplane takes off.
TCP in Action: Real-World Examples
TCP is behind much of the online activity that you do every day. It works in the background to make sure everything works the way it is supposed to. This makes your experience online seamless.
How TCP Supports Web Browsing
Every time you browse the internet, TCP is at work. It allows your browser to get information from web servers. Whether you are using Chrome, Firefox, or Safari, TCP is an essential part of the process that allows you to read your favorite websites and see videos.
- Establishing a Connection: Your browser uses TCP to request a connection with the web server.Before any information is sent, your browser initiates a three-way handshake to establish a secure connection.
- Requesting Data: Your browser sends a request to the server, asking for a webpage.The browser sends a request for a webpage. It’s like asking the library for a certain book.
- Receiving Data: The server sends back the webpage data in packets.The server slices the webpage into packets and sends them back to your computer via TCP.
- Reassembling the Page: TCP puts all of the packets back together, and the browser displays the webpage.TCP makes sure that all the packets arrive in the correct order, and the browser can then show the webpage as you expect it.
Without TCP, the web pages may arrive broken, or the data may arrive out of order. TCP ensures that your web browsing experience is smooth.
TCP in Email Communication
When sending emails, TCP is an integral part. It ensures your messages get to their destinations reliably. It’s a reliable way to ensure that your message arrives at the inbox.
- Sending the Email: Your email client uses TCP to send your message to the email server.The email client uses TCP to transmit the message. Think of it like putting your letter in the mailbox.
- Server Processing: The email server uses TCP to send the email to the recipient’s email server.The server receives the email. Then it uses TCP to forward the message to the intended recipient’s server.
- Receiving the Email: The recipient’s email server receives the email via TCP.The recipient’s email server confirms that the email has arrived and makes it available to the recipient.
- Viewing the Email: The recipient’s email client uses TCP to get the email from the server.The recipient’s email client retrieves the email from the server using TCP.
TCP guarantees that emails are sent in their complete form. If an email is cut off or has missing sections, it can cause miscommunication. TCP resolves this issue.
Advanced Concepts of TCP
Besides the core functions, TCP includes several advanced features that make it a robust and reliable protocol.
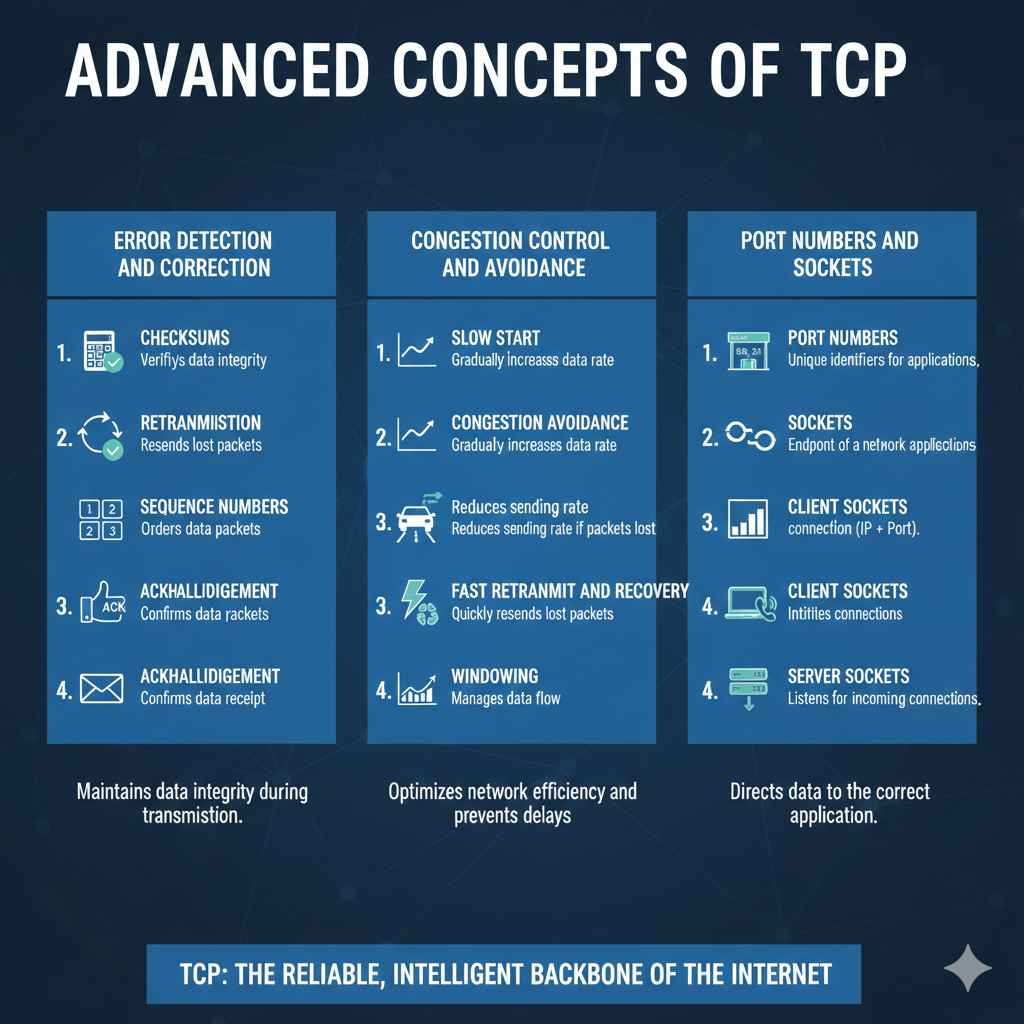
Error Detection and Correction
Error detection is a key task of TCP. It makes sure that data is not damaged or corrupted during transmission. TCP employs several techniques. This includes checksums and retransmission mechanisms.
- Checksums: TCP uses checksums to find errors.TCP computes a checksum for each packet. When the packet arrives, the receiver recomputes the checksum. If the checksums don’t match, it means there is an error.
- Retransmission: TCP automatically retransmits any packets that are lost or damaged.If the receiver does not acknowledge a packet, TCP assumes the packet was lost and sends it again. This helps guarantee that every part of the message arrives correctly.
- Sequence Numbers: Sequence numbers make sure the data arrives in order.Each packet has a unique sequence number. If packets arrive out of order, TCP will reorder them. It is similar to having numbered pages in a book to put them back in order.
- Acknowledgment: TCP uses acknowledgments to confirm the successful receipt of data.The receiver sends acknowledgments back to the sender. If the sender does not receive an acknowledgment within a certain amount of time, it resends the data.
These methods make sure that any damage during the transmission process is found. Then they can be fixed. Without error detection, data corruption could be a frequent event.
Congestion Control and Avoidance
Congestion control is essential for preventing network overload. TCP uses different ways to avoid congestion. When too much data is sent over a network, this can lead to delays. TCP manages the flow of data.
- Slow Start: TCP begins slowly and increases the data rate gradually.When a new connection starts, TCP starts by sending a few packets. Then it increases the data rate gradually. This is done to test the network’s capacity. Think of it like slowly increasing the volume on a speaker.
- Congestion Avoidance: If packets are lost, TCP decreases the sending rate.When the network is congested, TCP reduces the amount of data it sends. This avoids flooding the network. It’s like easing off the gas pedal to prevent an accident.
- Fast Retransmit and Fast Recovery: These methods improve recovery from packet loss.When multiple packets are lost, TCP quickly resends the lost packets. Fast Retransmit and Fast Recovery speed up the process of recovering from packet loss.
- Windowing: TCP uses a sliding window to manage data flow.TCP uses a sliding window to manage how much data the sender can send. This window size adjusts based on the receiver’s capacity and network congestion.
These controls help avoid network congestion. They provide a better experience. They make the internet efficient.
Port Numbers and Sockets
Port numbers and sockets are a key aspect of how TCP works. They make sure data is directed to the right app on your device. Every application uses a different port number.
- Port Numbers: Unique identifiers for different applications.Port numbers are like extensions in a building. They help differentiate between different applications that are running on a computer. For instance, port 80 is used for HTTP traffic. Port 21 is used for FTP.
- Sockets: Sockets are the endpoint of a network connection.A socket is a combination of an IP address and a port number. It represents a connection between two applications. Sockets allow applications to send and receive data via TCP.
- Client Sockets: Used by client applications to initiate a connection.Client sockets are the end of the connection initiated by a client. This is like the phone dialing the other end.
- Server Sockets: Used by server applications to listen for incoming connections.Server sockets wait for incoming connections from clients. These are waiting like a receptionist at a front desk.
Port numbers make sure that the right data reaches the right application. If a web server has all of its traffic going to the same port, then there can be no distinction. TCP uses port numbers to solve this issue.
| Feature | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Connection-Oriented | Establishes a connection before data transfer | Ensures reliable and orderly data delivery |
| Reliable Data Transfer | Guarantees that data is received without errors | Provides certainty that data arrives complete |
| Ordered Delivery | Ensures data packets are reassembled in the correct order | Allows applications to receive data in the original sequence |
| Flow Control | Manages the rate of data transmission to prevent overwhelming the receiver | Avoids congestion and ensures efficient network usage |
| Error Detection | Uses checksums and retransmission to detect and correct data errors | Maintains data integrity during transmission |
| Congestion Control | Manages the rate of data transmission to prevent network overload | Ensures fair network usage and avoids delays |
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What is the main job of TCP?
Answer: TCP’s main job is to ensure reliable and ordered delivery of data over the internet.
Question: How does TCP make sure data arrives in the correct order?
Answer: TCP uses sequence numbers to order the data. Packets are arranged based on these numbers.
Question: What is a port number?
Answer: A port number is a unique number that identifies a specific application or service on a device.
Question: What is a socket?
Answer: A socket is a combination of an IP address and a port number, representing a network connection endpoint.
Question: How does TCP handle errors?
Answer: TCP uses checksums to detect errors and retransmits any corrupted or lost data packets to guarantee all data is delivered correctly.
Final Thoughts
This exploration provides a clear view of how What Is Transmission Control Protocol in Computer Networks? TCP works. It breaks down the way data is sent, the steps TCP takes to make sure data is sent accurately, and the essential part that TCP plays in the modern internet. It emphasizes why TCP is used so much. It is the reason that you can browse the internet and send emails without interruptions. TCP makes the internet experience trustworthy.
If you’re interested in learning more, try experimenting with network tools or setting up your own small network. Exploring how the different parts work together can bring more clarity and create a deeper connection with how the internet works. That can make your knowledge even stronger. Keep learning, and you’ll be able to master the network environment!