If you’re wondering, What Does Transmission Control System MIL Request Mean?, you’re not alone! Many car owners find the check engine light (MIL) a bit of a mystery, especially when it’s related to the transmission. This can seem scary, but don’t worry. This guide breaks down what it means in simple terms. We’ll explore the basics and give you a step-by-step approach to figure out what’s happening. Ready to learn what that light is trying to tell you?
Decoding the Check Engine Light and Its Purpose
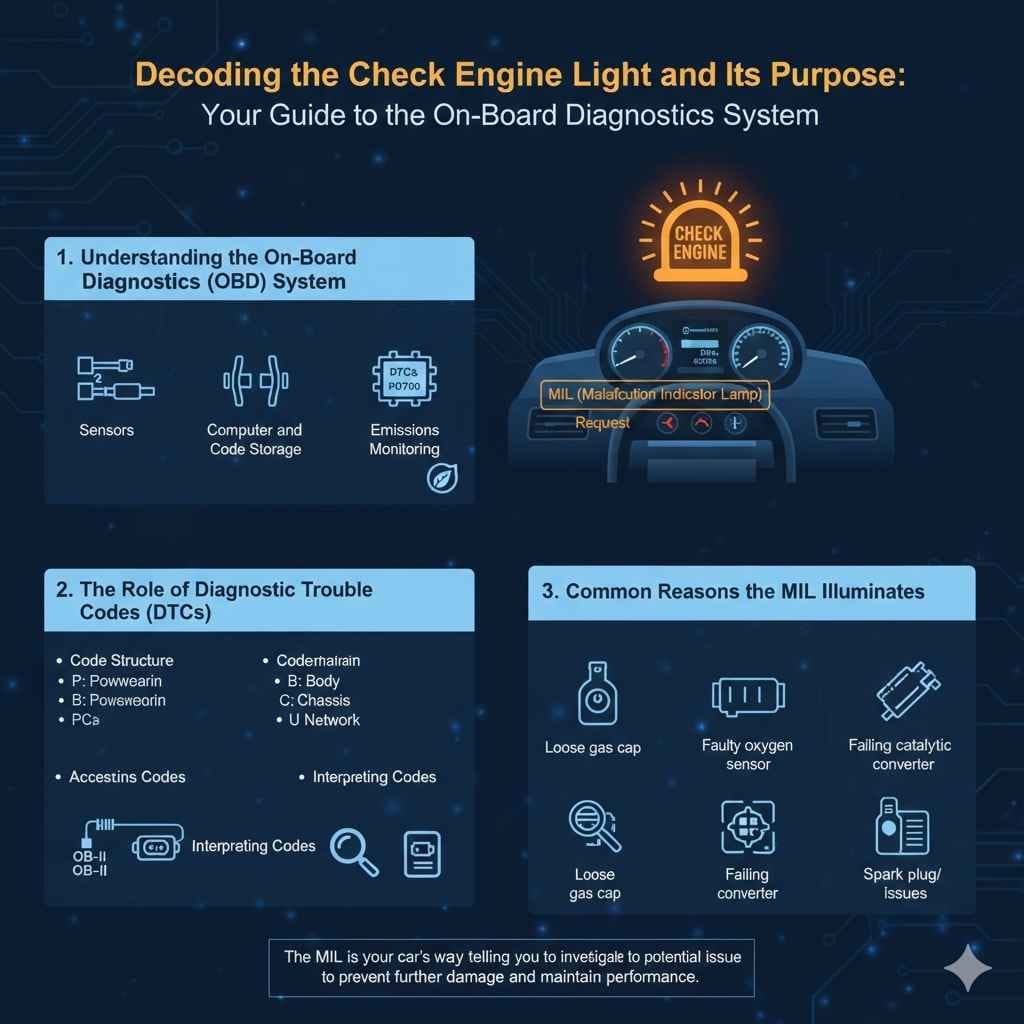
The check engine light, also known as the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), is a warning signal in your car’s dashboard. It’s a key part of your car’s on-board diagnostics (OBD) system. This system constantly monitors various components. When it detects a problem, the MIL turns on. This could be anything from a loose gas cap to a serious engine issue. The purpose of the MIL is to alert you to a potential problem that could affect your car’s performance or emissions. It’s a signal to investigate the issue promptly to prevent further damage or repair costs.
Understanding the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) System
The OBD system is a computer-based diagnostic system that monitors your car’s performance and emissions. It was introduced to help reduce air pollution and improve car efficiency. Sensors throughout your car send data to the car’s computer, which analyzes the information. If the computer detects a problem, it stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC). This code provides information about the specific issue. When the MIL illuminates, it’s accompanied by one or more DTCs. These codes help mechanics diagnose the problem quickly and efficiently. Modern OBD systems are complex, but they are designed to give us important information about car’s condition.
- Sensors: Your car has several sensors like the oxygen sensor, crankshaft position sensor, and mass airflow sensor. These sensors provide vital information to the car’s computer. The oxygen sensor measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The crankshaft position sensor monitors the position and speed of the crankshaft. The mass airflow sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine. This data helps the computer determine how to operate the engine and transmission.
- Computer and Code Storage: The car’s computer, the powertrain control module (PCM), processes the data from the sensors. It compares the sensor readings against pre-set parameters. If the readings are outside the expected range, the computer stores a DTC and activates the MIL. DTCs are specific codes that indicate the type of problem. For instance, a P0700 code often points to a transmission control system issue.
- Emissions Monitoring: The OBD system closely monitors your car’s emissions. It checks the catalytic converter, evaporative emissions system, and other components. If there’s an issue with the emissions system, the MIL will turn on. This is especially important for compliance with environmental regulations. Addressing emission problems helps protect the environment and ensures your car meets emission standards.
The Role of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
When the check engine light comes on, it’s usually accompanied by one or more DTCs. These codes are the language that your car uses to communicate with mechanics. DTCs are a series of letters and numbers (e.g., P0700). Each code is associated with a specific problem. Reading these codes with a scan tool allows mechanics to quickly identify the issue and begin repairs. While you can buy a basic code reader, more complex problems may require professional tools and expertise.
- Code Structure: DTCs follow a standardized format. The first letter identifies the system that the problem relates to. ‘P’ indicates powertrain (engine and transmission). ‘B’ indicates body. ‘C’ indicates chassis. ‘U’ indicates network communication. The next three digits provide more detail about the specific problem.
- Accessing Codes: To read the DTCs, you’ll need a scan tool. Scan tools connect to the OBD-II port. This port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. The scan tool will display the codes. Some scan tools also provide a brief description of the problem.
- Interpreting Codes: Once you have the code, you can research what it means. Online resources and repair manuals provide code definitions and troubleshooting steps. Keep in mind that a single DTC might have several causes. Therefore, professional diagnosis is often recommended.
Exploring “What Does Transmission Control System MIL Request Mean?”
When your MIL comes on and it relates to the transmission control system, it can mean a few different things. The transmission control system is a crucial part of your car, responsible for shifting gears smoothly and efficiently. Problems can range from minor software glitches to more serious mechanical issues. Addressing a transmission-related MIL request promptly is important to prevent further damage and ensure your car’s reliability. Let’s delve into what this might actually signify.
Transmission Control System Basics
The transmission control system (TCS) manages how your car’s transmission works. It’s composed of a series of components working together. These include the transmission control module (TCM), solenoids, sensors, and the transmission itself. The TCM is the “brain” of the system. It receives data from various sensors about vehicle speed, engine load, and throttle position. It uses this data to make decisions about when to shift gears. Then, the TCM sends signals to the solenoids. The solenoids control the hydraulic pressure in the transmission. This results in smooth gear changes. This system enhances fuel efficiency, performance, and the overall driving experience.
- Transmission Control Module (TCM): The TCM is a specialized computer that oversees the transmission. It receives information from various sensors and then controls the shifting of gears. The TCM is programmed with specific instructions to control gear changes under different conditions. The TCM is often integrated with the powertrain control module (PCM).
- Solenoids: Solenoids are electromagnetic valves that control the flow of hydraulic fluid within the transmission. They respond to signals from the TCM. The solenoids open and close to change the fluid pressure. That allows for the gear changes in automatic transmissions. Solenoids are vital in ensuring that gears shift smoothly and accurately.
- Sensors: Various sensors provide the TCM with vital information. This includes vehicle speed sensors, input and output speed sensors, and throttle position sensors. The TCM uses this data to make sure that gear changes happen at the correct time. The sensors’ data guarantees that the transmission operates effectively under all driving conditions.
Common Causes Behind the MIL Request
Several issues can cause the check engine light to come on with a transmission-related fault. Some issues are relatively minor. Others might require more involved repairs. Identifying the source of the problem is the first step toward a solution. Common causes include electrical issues, sensor problems, and issues within the transmission itself. Knowing these potential causes helps you better understand the situation and make informed decisions about repairs. These can involve problems with the transmission fluid or a software update.
- Sensor Malfunctions: Faulty sensors are a common cause of transmission-related DTCs. Sensors monitoring vehicle speed, transmission input/output speeds, or throttle position can fail. These sensors provide vital data to the TCM, and a failure can trigger the MIL.
- Solenoid Issues: Solenoids control the hydraulic pressure for gear changes. Issues with solenoids, such as a clogged valve or electrical failure, can cause shifting problems. This can include delayed or harsh shifts. Solenoid problems often trigger a DTC.
- Transmission Fluid Problems: Low, dirty, or contaminated transmission fluid can lead to various transmission problems. Fluid helps lubricate and cool the transmission components. When the fluid is bad, it can cause the transmission to overheat or experience mechanical damage. Regular fluid checks and changes are key to avoiding these problems.
Troubleshooting Steps When the MIL Appears
When the MIL illuminates and the issue appears to be related to the transmission, it’s essential to follow a systematic approach. This helps you to identify the problem accurately and avoid unnecessary repairs. This involves a few key steps. First, you’ll need to use a scan tool to retrieve the DTCs. Secondly, you’ll need to inspect the transmission fluid and check for leaks. Finally, you can consult with a mechanic.
Using a Scan Tool and Code Interpretation
A scan tool is your essential tool for diagnosing a transmission problem. Scan tools connect to your car’s OBD-II port and read the DTCs. This step is essential to understanding the issue. Once you have the code, you can research the meaning of the specific code. You can find this information online or in a repair manual. The code gives you a clue about the component or system that is the source of the problem. However, knowing the code is just the first step. More investigation is often needed.
- Code Retrieval: Connect the scan tool to the OBD-II port. This port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Turn the ignition on (without starting the engine). Follow the scan tool’s instructions to retrieve the codes.
- Code Lookup: Once you have the DTCs, look them up using online resources. Many websites and databases provide definitions for DTCs. These definitions will help you identify the component or system associated with the code.
- Data Analysis: Some advanced scan tools provide live data. This data shows the values from the sensors in real-time. Analyzing this data can help you identify a sensor malfunction. A good mechanic may look at several data points to diagnose the issue more thoroughly.
Inspection and Preliminary Checks
Before any major repairs, perform a basic inspection. This can often help you identify simple problems. The first check should involve transmission fluid. Check the fluid level and its condition. Look for leaks around the transmission. These preliminary steps can save you time and money. They can help avoid more extensive investigations.
- Transmission Fluid Check: Check the transmission fluid level using the dipstick. Make sure the fluid is within the recommended range. Check the color and smell of the fluid. Dark, burnt-smelling fluid may indicate a problem.
- Leak Inspection: Look for any signs of fluid leaks. Check under the car for any spots. Inspect the transmission case, seals, and lines for leaks. A leak can cause low fluid levels and lead to transmission damage.
- Wiring and Connector Inspection: Check the wiring and connectors related to the transmission. Look for any damage to the wiring or corrosion on the connectors. Corrosion can affect the signals sent to and from the TCM.
Seeking Professional Assistance
While you can do some troubleshooting yourself, some situations require professional expertise. For instance, more complex issues or mechanical problems require specialized tools and knowledge. A professional mechanic can perform a thorough diagnosis and make necessary repairs. Your car is a complex machine, and a professional can ensure the repairs are done correctly.
When to Consult a Mechanic
Knowing when to call a mechanic can save you time and prevent potentially costly mistakes. If you are uncomfortable working on your car, it is wise to consult a mechanic. If the problem seems complex or the code suggests a significant issue, professional help is important. The mechanic will have the tools and experience to properly diagnose and fix the problem. They can assess the issues correctly.
- Complex DTCs: If the DTC indicates a complicated issue, it is time to call a mechanic. Codes related to internal transmission components or electrical problems are best handled by a professional.
- Shifting Issues: If your car is experiencing shifting problems, a mechanic can help. This includes rough shifts, delayed shifts, or slipping gears. These problems can cause serious damage to your transmission.
- Noisy Transmission: Any unusual noises coming from your transmission, like clunking or whining, require attention from a mechanic. A mechanic can properly diagnose and address the issues. They can prevent further damage.
Choosing a Reputable Mechanic
Choosing the right mechanic is crucial for ensuring that your car is properly repaired. Look for mechanics with experience working on transmissions. Check online reviews and ask for recommendations from friends. A good mechanic should be certified. A good shop will explain the problem clearly and provide a written estimate. They should also be able to answer any of your questions about the repair process.
- Qualifications and Certifications: Check that the mechanic is certified by organizations like ASE (Automotive Service Excellence). ASE certifications show they have the knowledge and experience.
- Reviews and Recommendations: Look for shops that have good reviews. Talk to people you trust for recommendations. This can help you find a mechanic who provides great service.
- Transparency and Communication: A good mechanic will explain the problem clearly. They will provide a detailed estimate before starting any work. They should also keep you informed about the progress of the repairs.
Transmission Control System MIL Request Examples
- Scenario 1: Your check engine light comes on, and a scan reveals a P0700 code. This points to a transmission control system malfunction. You check your transmission fluid and find it’s low. Adding fluid solves the problem.
- Scenario 2: The MIL is on, with a P0720 code. This indicates an output speed sensor malfunction. After replacing the sensor, the MIL goes away and the transmission shifts correctly again.
- Scenario 3: The check engine light appears, showing a P0751 code. The mechanic finds a faulty shift solenoid. After replacing the solenoid, your car’s shifting issues are resolved.
| Issue | DTC | Possible Cause | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shift Issues | P0700 | TCM Problem | Professional Diagnosis |
| Delayed Shifting | P0720 | Output Speed Sensor | Sensor Replacement |
| Harsh Shifting | P0751 | Shift Solenoid Issue | Solenoid Replacement |

Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What does P0700 mean?
Answer: P0700 is a generic code that indicates a transmission control system malfunction. It often signals a problem within the TCM itself.
Question: Can I drive my car with the check engine light on due to a transmission issue?
Answer: It’s best to avoid driving extensively with a transmission issue. Get the issue diagnosed and fixed as soon as possible to avoid further damage.
Question: What are the common symptoms of a transmission problem?
Answer: Common symptoms include harsh or delayed shifting, slipping gears, unusual noises, and the check engine light illuminating.
Question: How often should I change my transmission fluid?
Answer: It is important to refer to your car’s owner’s manual for specific recommendations. Generally, a transmission fluid change is recommended every 30,000 to 60,000 miles.
Question: Can a simple software update fix a transmission problem?
Answer: Sometimes, a software update can resolve certain transmission issues. However, mechanical problems may require more extensive repairs.
Final Thoughts
Dealing with a check engine light related to the transmission can seem tough, but it doesn’t have to be. Understanding What Does Transmission Control System MIL Request Mean? is the first step. You’ve now seen how the system works and common issues. You’ve also learned about diagnostics. If you have the right tools, you can handle some basic checks. When it gets complex, consulting a mechanic is the best move. Remember, taking action quickly can prevent more significant problems and expenses down the road. Addressing any issues when they arise helps maintain your car’s value and ensures a smooth driving experience. So, stay calm, gather information, and take appropriate steps. Doing so will ensure your car runs at its best.

