It can feel overwhelming to learn about Most Effective Ways to Control the Transmission of Infection. For beginners, it’s easy to get confused by all the medical terms and different types of infections. Don’t worry! This guide will break things down in simple terms. We’ll walk through a straightforward, step-by-step plan to help you grasp the essential actions. You’ll learn how to take charge of your health and the health of those around you. Let’s start by looking at some basic concepts.
Understanding How Germs Spread
The spread of infections happens because germs, such as viruses and bacteria, move from one place to another. This movement can be pretty simple, and that’s why knowing the paths these germs take is so important. Things like coughing, sneezing, touching contaminated surfaces, or even close contact with someone who’s sick can all spread germs. Think of it like a chain reaction. A single germ can start a whole spread of illness if you don’t take the right steps. This is why knowing how germs move is the first, key piece of information.
Types of Germs Causing Illness
Different germs cause different illnesses. They all have their own unique ways of spreading and affecting our bodies. Understanding these germs is key to knowing the best ways to protect ourselves. Let’s explore some of the most common types of germs. This awareness will help make the other steps we take make even more sense.
- Viruses: Viruses are tiny organisms that need a host cell to reproduce. They’re responsible for illnesses like the common cold, the flu, and COVID-19. They often spread through the air or by direct contact. Viruses are frequently spread through respiratory droplets created when someone coughs, sneezes, or talks. For example, the influenza virus travels in this way.
- Bacteria: Bacteria are single-celled organisms. They can cause a wide variety of infections, such as strep throat or food poisoning. They can be found everywhere, but some are harmful to humans. These spread through contact, contaminated food, or through insect bites. For example, some bacteria spread when people do not wash their hands after using the restroom.
- Fungi: Fungi are organisms like molds or yeasts, and some can cause infections. These can include ringworm or athlete’s foot. Fungi can be found in the environment and are often spread through contact with infected surfaces or people. For instance, you could pick up a fungus by walking barefoot in a public shower.
- Parasites: Parasites live on or in a host organism and get their food from them. These include things like worms or protozoa. Parasites spread through contaminated food or water, insect bites, or direct contact. For example, malaria is spread by mosquitos.
How Germs Move From One Place to Another
Germs use several paths to move around and infect people. Knowing these paths is important for stopping the spread. The primary ways germs move from one place to another are through direct contact, indirect contact, droplets, and airborne transmission. Recognizing these different methods allows for the proper selection of control measures, so that infection doesn’t spread. We’ll explore these methods in detail to understand them better.
- Direct Contact: This happens when you have physical contact with someone who is sick or with their bodily fluids. This could be as simple as shaking hands, kissing, or sharing a drink. It is a common way for infections to spread. Many bacterial infections, like those causing skin infections, move this way.
- Indirect Contact: This is when you touch something that has germs on it, such as a doorknob or a phone, and then touch your face. Surfaces become contaminated when people touch them after they have come into contact with the germ. Then, those surfaces can pass that to someone else.
- Droplet Transmission: Droplets are larger particles that are produced when someone coughs, sneezes, or talks. These droplets can then land in someone’s mouth or nose, or be inhaled into the lungs. Influenza and the common cold often spread through these droplets.
- Airborne Transmission: Some germs can stay in the air for longer periods. This happens with very small particles that can travel long distances. This type of transmission is common with viruses like measles or chickenpox.

The Crucial Role of Hand Hygiene
Hand hygiene is a simple yet powerful way to avoid infection spread. Washing your hands properly is one of the most effective actions to remove germs. It protects not only you but also those around you. This is a foundational practice in stopping the transmission of illness. It prevents the spread of germs by physically removing them from your hands. Regular and proper handwashing breaks the chain of infection and keeps communities healthier. It’s a proactive step that is accessible to everyone.
When to Wash Your Hands
Knowing when to wash your hands is just as important as knowing how to wash them. There are certain times when washing hands is particularly necessary to help stop the transmission of germs. Following this schedule will keep you and the people around you safer. This is about making it a habit so that it becomes second nature.
- Before Eating or Preparing Food: Before you start preparing or eating food, you want to wash your hands to prevent any germs from contaminating your meal or entering your body. This avoids spreading germs from your hands to your food, which is a common path of transmission.
- After Using the Restroom: This is one of the most critical times. After using the bathroom, washing your hands removes any germs you may have picked up. This includes washing them after you use the toilet, before and after you change a diaper, or after you help a child with toilet hygiene.
- After Coughing or Sneezing: Coughing and sneezing can release germs into the air and onto your hands. Washing your hands after these actions removes these germs. This action can then prevent the transmission to others or to surfaces that you may touch.
- After Touching Public Surfaces: Surfaces like doorknobs, handrails, and public transportation seats are full of germs. Washing your hands after touching them prevents germs from entering your body. This is a step to take especially during flu season.
- After Contact with Animals: Animals can carry germs. Washing your hands after petting an animal, cleaning up after your pet, or visiting a petting zoo reduces your risk. This also helps with minimizing risks like Salmonella or E. coli.
How to Wash Your Hands Correctly
Washing your hands is simple, but the process has to be done correctly to be effective. This is how you should wash your hands. Following this simple guide will help you to remove the most germs.
- Wet Your Hands: Start by wetting your hands with clean, running water, which can be warm or cold.
- Apply Soap: Apply enough soap to cover all surfaces of your hands.
- Lather: Rub your hands together, making sure to lather the backs of your hands, between your fingers, and under your nails.
- Scrub: Scrub your hands for at least 20 seconds. A good rule of thumb is to hum the “Happy Birthday” song twice.
- Rinse: Rinse your hands well under running water.
- Dry: Dry your hands using a clean towel or air dry them. If using a public restroom, use a paper towel to turn off the faucet and open the door.
Creating Clean Spaces and Places
Clean environments are key to preventing the spread of infection. From your own home to public spaces, keeping surfaces clean minimizes the presence of germs. This part explores easy ways you can promote clean spaces. By understanding the importance of cleaning and disinfecting, we can make spaces safer for everyone. We can turn a place from a source of germs into a healthier environment by taking a few steps.
Cleaning vs. Disinfecting: What’s the Difference?
There is a difference between cleaning and disinfecting. Each process targets germs in different ways. Knowing this difference is key to how you maintain a healthy environment. Each has a specific function in reducing the presence and impact of germs.
- Cleaning: Cleaning removes dirt, debris, and some germs from surfaces. It’s done with soap and water. Cleaning physically removes particles, which can help reduce the number of germs. Cleaning doesn’t kill germs.
- Disinfecting: Disinfecting uses chemicals to kill germs on surfaces. Disinfectants are designed to kill many types of germs, but they don’t necessarily clean away dirt and debris. Disinfecting is often used after cleaning a surface to ensure that any remaining germs are eliminated.
Cleaning and Disinfecting Your Home
Your home should be your safe space. Regular cleaning and disinfecting can help create a healthier home environment. Certain areas need more attention. This will help you keep the germs at bay. This protects the health of your family.
- High-Touch Surfaces: These are surfaces that people touch frequently, like doorknobs, light switches, countertops, and remote controls. Clean and disinfect these surfaces daily, particularly during cold and flu season.
- Bathrooms: Bathrooms are prone to moisture, which is a breeding ground for germs. Clean and disinfect your bathroom at least once a week. Pay close attention to the toilet, sink, shower, and floor.
- Kitchen: The kitchen is another area where germs can spread quickly. Clean and disinfect countertops, sinks, and cutting boards regularly. Make sure to clean up spills immediately.
- Laundry: Wash your clothes, towels, and bedding frequently, especially if someone in your home is sick. Use hot water and the correct amount of detergent. This also applies to things like dishcloths and sponges.
Vaccinations and Their Impact
Vaccinations are a powerful tool for preventing the spread of many diseases. Vaccines teach your body how to fight off certain infections. This prevents you from getting sick and limits the spread of disease. Many illnesses can be avoided with vaccines. Vaccines protect not only you but also those around you by creating “herd immunity.” This immunity means that when many people in a community are vaccinated, it is harder for a disease to spread. This protects those who are most vulnerable, like babies and people with weakened immune systems.
How Vaccines Work
Vaccines work by training your immune system. They do this without making you sick. Vaccines help your body create a defense against specific germs. When a germ enters your body, your immune system recognizes it and creates antibodies. These antibodies help to kill the germ or stop it from causing illness. Vaccines contain either a weakened or inactive form of the germ. The body can then develop immunity without the person getting the disease.
- Introduction: Vaccines introduce a weakened or inactive version of a germ into your body. This triggers your immune system to create antibodies without causing illness.
- Antibody Production: Your immune system recognizes the germ and produces antibodies. These antibodies are like your body’s personal army, ready to fight off the infection.
- Immune Memory: Your body creates memory cells. These cells remember the germ and can quickly produce antibodies if you’re exposed to it again in the future.
Vaccine Schedules and Recommendations
Vaccination schedules help us to stay protected from many diseases. Healthcare providers follow schedules of when to give certain vaccines. Keeping up-to-date with your vaccinations is an important action for safeguarding your health. The schedules are made to provide you with the best protection at the right times. Your healthcare provider can guide you on the vaccines that are right for you.
For example, children receive a series of vaccinations from a young age to protect them from diseases like measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR). Adults are encouraged to receive yearly flu shots and boosters for diseases like tetanus and whooping cough.
Using Protection Measures When Needed
Protection measures such as masks and gloves can be effective ways of reducing the transmission of infection, in certain situations. They act as barriers. This is especially useful in high-risk environments. This can prevent the spread of germs. These tools are important, and knowing when and how to use them can make a big difference in keeping people safe. By using these measures, you are taking an active part in creating safer situations.
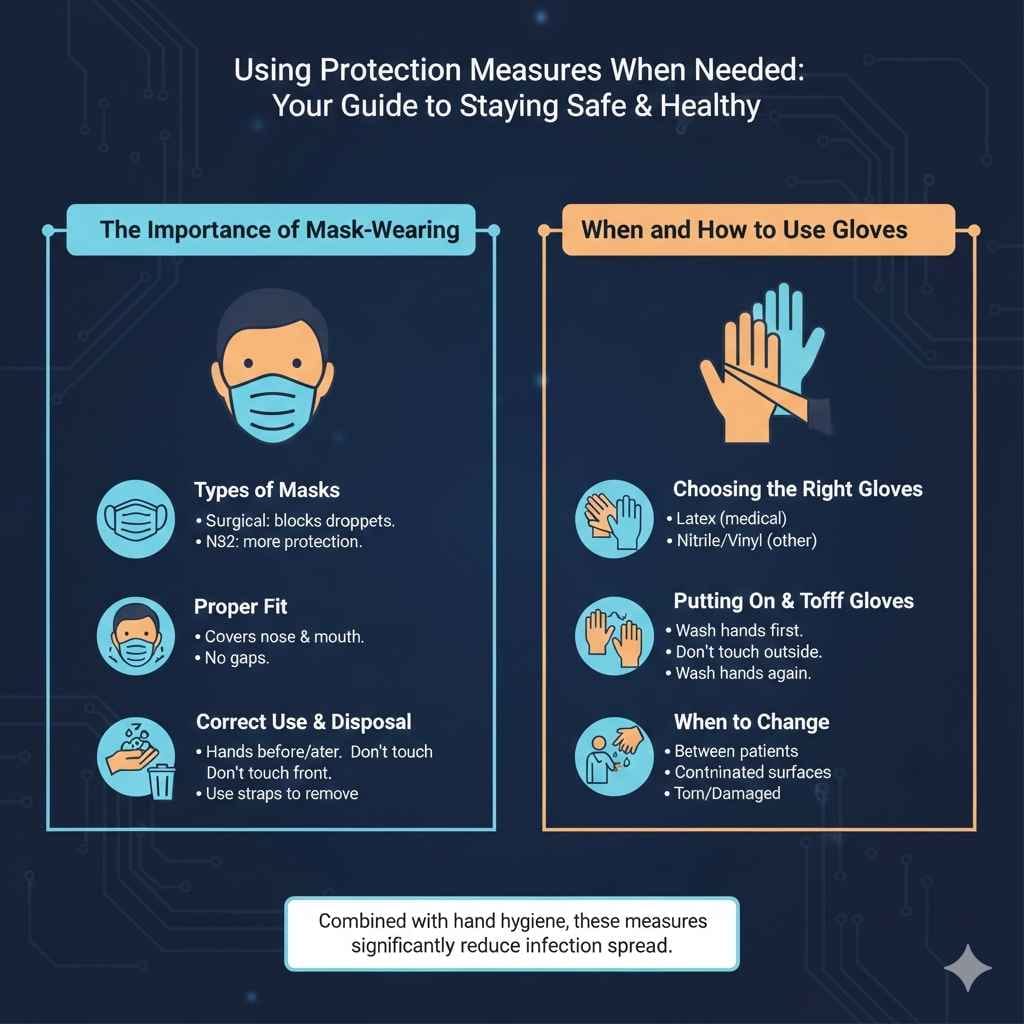
The Importance of Mask-Wearing
Masks are essential for blocking the spread of respiratory germs. Masks help to stop droplets from coughs, sneezes, and talking from traveling into the air and infecting others. They are most useful when you are sick. When worn correctly, masks are a good way of protecting both the person wearing them and those around them. Masks aren’t a perfect shield, but they do make a big difference, especially when used in combination with other preventive measures.
- Types of Masks: There are several kinds of masks. Each offers different levels of protection. Surgical masks protect against large droplets, while N95 respirators offer more protection.
- Proper Fit: Ensure the mask covers your nose and mouth. The mask should fit snugly against your face, with no gaps.
- Correct Use and Disposal: Put on the mask before entering a risky situation, and don’t touch the front of the mask. Remove it by the straps, and wash your hands.
When and How to Use Gloves
Gloves are especially used in certain professions. They help create a barrier. Gloves are most frequently worn when people may come in contact with bodily fluids, or when handling items that could be contaminated. It’s important to use gloves correctly to make sure that they are effective. The right use of gloves is an important step to keeping things safe.
- Choosing the Right Gloves: Select gloves that fit the task. Latex gloves are often used for medical procedures. In other environments, other materials, like nitrile or vinyl, may be preferred.
- Putting On and Taking Off Gloves: Wash your hands before putting on gloves. Carefully remove gloves, being sure not to touch the outside, and wash your hands again.
- When to Change Gloves: Change gloves when moving from one patient to another, after touching contaminated surfaces, and if they get torn or damaged.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: How long should I wash my hands?
Answer: You should wash your hands for at least 20 seconds. Hum the “Happy Birthday” song twice to help track the time.
Question: Are hand sanitizers as effective as washing with soap and water?
Answer: Hand sanitizers with at least 60% alcohol are very effective at killing germs when soap and water aren’t available. But, washing with soap and water is still generally preferred.
Question: What’s the best way to clean surfaces at home?
Answer: Clean surfaces with soap and water first to remove dirt and debris. Then, use a disinfectant to kill germs.
Question: Can vaccines cause the illness they are designed to prevent?
Answer: No, vaccines cannot cause the illness they are designed to prevent. They contain either weakened or inactive germs.
Question: How can I protect myself from germs in public spaces?
Answer: Wash your hands frequently, avoid touching your face, and use masks and gloves when necessary.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and applying Most Effective Ways to Control the Transmission of Infection doesn’t have to be hard. By focusing on simple actions like hand hygiene, regular cleaning, and vaccinations, you can make a major impact on your own health and the safety of those around you. We’ve explored the paths germs take, the importance of cleaning and disinfecting, and the amazing impact of vaccines and protective gear. Remember, every action matters, from washing your hands correctly to staying up-to-date with your vaccinations. Put these steps into practice. Take charge of your health and the health of your community. Stay informed, stay safe, and help stop the spread of infection!