Lots of folks find learning How to Program a Transmission Control Module Correctly a bit tricky when they first start. It’s common to feel unsure about where to begin. But don’t worry! This guide will break it all down in easy-to-follow steps. We’ll explore everything from the basic tools you will need, to how to test your work. We’ll guide you through each piece of the process, making sure you grasp every aspect. Let’s get started!
What You Need to Begin Programming
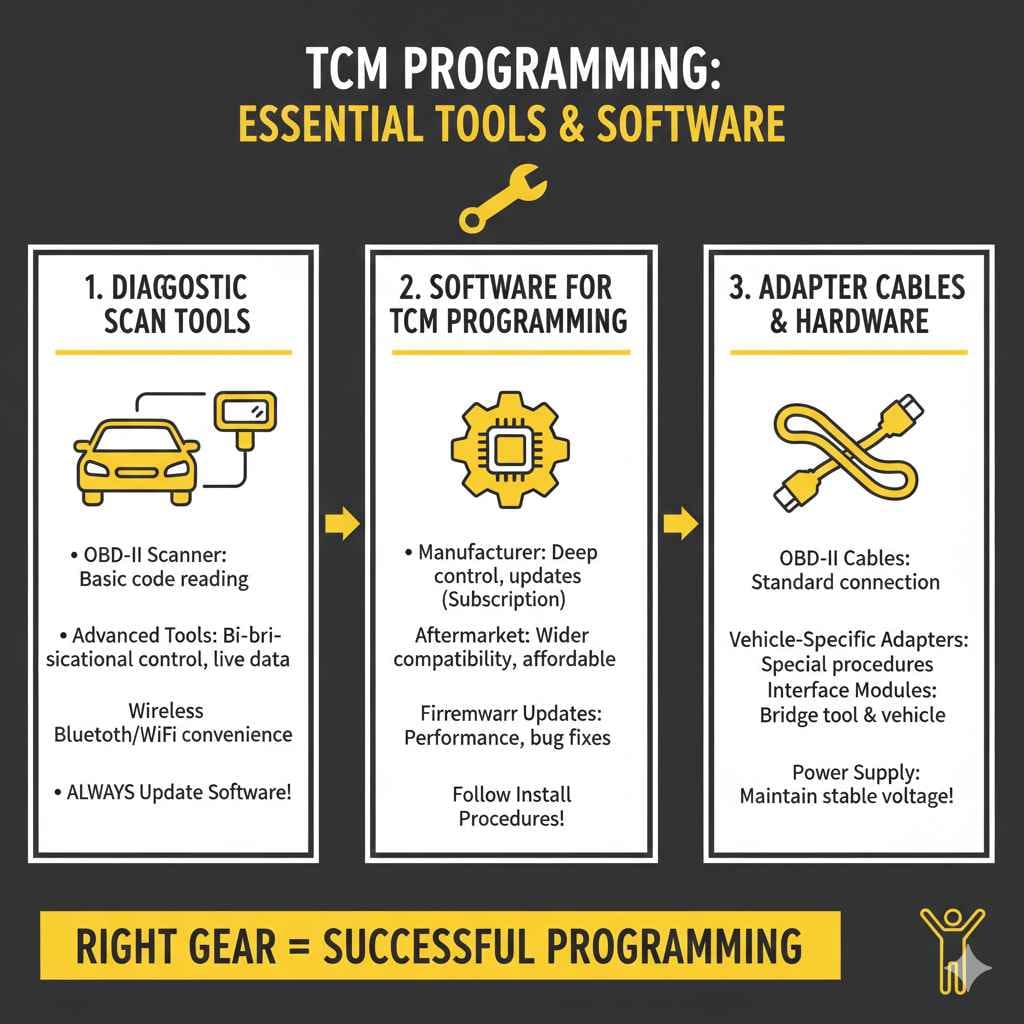
Before you even think about connecting to a Transmission Control Module (TCM), you need the right gear. Think of it like a mechanic’s toolbox – you can’t fix a car without the right tools! This includes hardware and software. Each piece plays a specific role in allowing you to program or reprogram the TCM correctly. Without the right equipment, the process will be impossible. This section outlines everything you need, from the essential diagnostic tools to the specific software and adapter cables that enable proper TCM programming.
Diagnostic Scan Tools Explained
A diagnostic scan tool is your window into the vehicle’s systems, allowing you to read trouble codes, view live data, and, most importantly, communicate with the TCM. Many different scan tools are available, ranging from basic code readers to advanced professional-grade units. Choosing the right one depends on your needs and budget. A basic code reader will typically only read and clear error codes. More advanced tools, however, give you access to a wider array of functions, including the ability to reprogram the TCM, read live data streams (crucial for diagnosing issues), and perform specific tests.
- OBD-II Scanner Basics: The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD-II) port is standard on most vehicles from the early 1990s onward. This is where you plug in your scan tool. A basic OBD-II scanner can read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), which are essential for identifying the source of many issues.
- Advanced Scan Tools: For more in-depth programming and diagnostics, you’ll need a more advanced scan tool. These tools often have enhanced features like bi-directional control (allowing you to command the vehicle’s systems) and the ability to display live data in a graphical format. You can often see the current operating parameters of the TCM, like shift points or pressure data.
- Wireless Connectivity Options: Some modern scan tools offer wireless connectivity, such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. This allows for easier use in the workshop. It also allows software updates to be delivered without needing to connect your tool to a computer with a cable. This is a very convenient option for many auto mechanics and enthusiasts.
- Importance of Software Updates: Keeping your scan tool’s software up to date is extremely important. Vehicle manufacturers regularly release updates to address bugs, add new features, and expand the range of vehicle models supported. Make sure your tool is always running the latest version.
Software for TCM Programming
Alongside the scan tool, you’ll need software capable of interacting with the TCM. This software can come in several forms, from specific manufacturer software to more versatile aftermarket solutions. The software is the brains of the operation. It interfaces with the TCM and allows you to load new programs, make adjustments, and perform calibrations. Choosing the right software often depends on the make and model of the vehicle you are working on. This section guides you through the types of software available and the steps to ensure compatibility and correct usage.
- Manufacturer Software: This is software provided by the vehicle manufacturer. It is often the most comprehensive option, as it is designed specifically for that brand’s vehicles. Manufacturer software can be expensive, and it may require a subscription to access updates and support. However, it often provides the deepest level of control and functionality.
- Aftermarket Software: Several aftermarket software packages are available. These may be more affordable than manufacturer software. They also offer wider vehicle compatibility. Aftermarket software can be a good choice for people working on a variety of vehicles. Make sure your chosen software is compatible with your scan tool.
- Firmware Updates: The software in your scan tool, as well as the TCM itself, will need periodic updates. These updates are typically available from the manufacturer. They can address issues, add new features, and improve overall performance.
- Installation Procedures: Installing the software correctly is key. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Incorrect installation can lead to problems during the programming process. It could even brick the TCM. Most software packages come with detailed documentation and support resources.
Adapter Cables and Hardware
You may also need special adapter cables and hardware to connect the scan tool to the vehicle. This is particularly true for older vehicles or for certain specialized programming procedures. Adapter cables ensure that the scan tool can properly communicate with the vehicle’s computer systems. Without the right cable, you will not be able to get connected, regardless of how advanced your scan tool or software is. It is important to know which cables you need ahead of time. This section explores different cable types and what they are used for, ensuring you have everything you need before starting the process.
- OBD-II Cables: These are the standard cables used for connecting to the OBD-II port. While often included with your scan tool, it is always a good idea to have a spare on hand.
- Vehicle-Specific Adapters: Certain vehicles or programming procedures may require special adapters. These adapters are made for a specific make or model. Always check the vehicle’s service information to determine if any special adapters are required.
- Interface Modules: Some advanced programming operations need an interface module. These modules serve as a bridge between the scan tool and the vehicle. They provide extra power or specialized communication protocols.
- Power Supply: During long programming sessions, the vehicle’s battery can drain. To avoid this, use a battery charger or a power supply to maintain a stable voltage. This prevents interruptions during programming that can corrupt the TCM.
Getting Ready to Program the TCM
Once you have all the necessary equipment, it’s time to prepare your vehicle and the TCM for programming. These steps are designed to ensure a smooth and safe process. The procedures cover how to find the TCM in your vehicle, secure your work area, and back up the existing data. Proper preparation is essential to prevent any errors during the programming phase. Neglecting these steps can lead to problems. This section details each of these important preparation steps for successful TCM programming.
Finding the TCM’s Location
The first step is locating the TCM. The location varies between vehicle makes and models. The TCM may be under the dashboard, in the engine compartment, or even in the transmission itself. The vehicle’s service manual or a quick online search can provide this info. Knowing where the TCM is located will allow you to access it and make the necessary connections. This section includes tips on how to identify the TCM’s specific location based on the vehicle’s make and model. You will want to be sure you are working with the correct component.
- Consult the Service Manual: The vehicle’s service manual is the best resource for finding the TCM. It will provide the exact location and any specific access instructions.
- Online Resources and Forums: Many online forums and websites are dedicated to specific vehicle makes and models. You can often find photos and detailed instructions on locating the TCM.
- Common Locations: While the exact location varies, TCMs are often found under the dashboard, in the engine compartment, or inside the transmission case. They are often near the engine control unit (ECU).
- Using VIN Lookup: Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) lookup tools can sometimes provide information about your car’s components. These tools are often available on automotive websites.
Preparing Your Work Area
A clean and organized work area is essential for a successful programming session. It reduces the chance of making mistakes or damaging any components. Prepare the vehicle and the surrounding environment to minimize the chance of errors. This includes making sure the car has enough battery power, and protecting the vehicle. This section guides you through the steps to set up your work area properly. This will make the programming process safer and easier.
- Vehicle Power: Ensure the vehicle’s battery is fully charged. Or, connect a battery charger or power supply to maintain a stable voltage throughout the process. This prevents interruptions.
- Safety Precautions: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical components. This reduces the risk of electrical shock or damage to the TCM.
- Environmental Factors: Work in a well-ventilated area. Protect the vehicle from the elements. Make sure you have adequate lighting.
- Organizing Your Tools: Keep your tools and equipment organized. Have everything within reach to avoid interruptions and minimize the chance of errors.
Backing Up Existing Data
Before any programming, back up the TCM’s existing data. This is an important safety step. It allows you to restore the original settings if something goes wrong during the programming process. Backing up the existing data is like creating a safety net. This is the only way you can undo any mistakes or problems. This section explains the process of backing up the existing TCM data. It also details the tools and steps needed to ensure a safe and secure backup.
- Using the Scan Tool: Most scan tools have a function to read and save the TCM’s existing data. Follow your scan tool’s instructions. This usually involves selecting the “Read” or “Backup” option.
- Saving the Data: Save the backed-up data to a safe location, such as your computer. This will allow you to access it again if you need it.
- Verification: Always verify the backup data by comparing it to a known good copy. This can help you make sure that the data is accurate.
- Documenting the Process: Keep a record of the backup process, including the date, time, and any settings you may have adjusted. This is useful for troubleshooting.
Correctly Programming the TCM Step by Step
With all the preparation completed, you can now start the actual programming process. This step is about loading new software onto the TCM. These steps are precise and need to be followed correctly to avoid any problems. These instructions provide a detailed guide on how to perform the programming, from starting the process to verifying the results. Always read the instructions that come with your specific scan tool and software to make sure you follow any special instructions.
Connecting to the TCM
Connect the scan tool and any necessary adapters to the vehicle. The quality of this connection is important. It determines the communication success between the scan tool and the TCM. The proper connection ensures that the data can be transferred and that the programming is done successfully. This section guides you through the process of correctly connecting the scan tool to the TCM. It covers the necessary steps to make sure your setup is ready to go.
- Locate the OBD-II Port: Find the OBD-II port on your vehicle. It is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Connect the Scan Tool: Plug the OBD-II connector from your scan tool into the OBD-II port.
- Power Up the Scan Tool: Turn on the scan tool. Make sure it powers up and connects to the vehicle.
- Check Connections: Make sure all connections are secure. Sometimes, even the smallest problem can interfere with data transfer.
Software Upload and Configuration
Once you are connected, load the new software onto the TCM. This involves using the scan tool and the accompanying software to upload the correct program file. This step is important for updating the transmission’s control strategies. The process can vary based on the specific scan tool and the vehicle. This section explains how to upload the software. It also helps you configure any settings to match your vehicle’s specifications. Always follow the prompts and instructions provided by the software.
- Selecting the Correct File: Choose the right software file for your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Incorrect software can cause many problems.
- Following On-Screen Prompts: Follow the instructions displayed on your scan tool. These will lead you through the programming steps.
- Entering Security Codes: Some programming procedures may require you to enter security codes or authorization keys. These codes are provided by the vehicle manufacturer or the software provider.
- Monitoring Progress: Keep a close eye on the programming progress. The scan tool will display the status. This confirms that the programming is happening correctly.
Testing and Verification
After the programming is finished, test the TCM to make sure it is working correctly. This is a critical step. It confirms that the new software has been successfully installed and that the transmission functions properly. Testing and verification may involve running diagnostic tests, monitoring live data, and performing road tests. These help identify any problems and ensure that the transmission performs as expected. This section helps you check the results of your work. It also provides tips on what to look for when verifying and how to resolve any issues.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Check for any new or existing DTCs. Clearing any codes can help identify problems.
- Live Data Monitoring: Use your scan tool to view live data. Monitor things like shift points, pressure readings, and other parameters. Make sure they match the expected values.
- Test Drives: Take the vehicle for a test drive. Pay attention to how the transmission shifts. Ensure it performs smoothly under different driving conditions.
- Reviewing the Software: Make sure that the software you uploaded is up to date and compatible with your car. This often helps you prevent future problems.
Common Programming Problems and Solutions
Even when following all the steps, you may face problems while programming. Programming can be a complex process. You might run into connection problems, incorrect software, or even software glitches. It is very useful to know how to resolve them. The section explores the challenges you might meet and offers ways to solve them. By being prepared, you can resolve problems more efficiently and ensure a successful programming outcome.
Troubleshooting Connection Problems
Connection problems can be very frustrating. They prevent the scan tool from communicating with the TCM. These issues can range from simple loose connections to more complex problems like damaged wiring. This part explains how to find and resolve common connection problems. By carefully checking the connections, you can ensure a reliable data transfer. This part provides easy steps to troubleshoot and fix connection issues, making sure you can get the programming process going.
- Check the OBD-II Port: Inspect the OBD-II port for any damage or debris. Clean the port if needed.
- Inspect Cables and Adapters: Examine all cables and adapters for wear and tear. Replace any damaged cables.
- Verify Power Supply: Make sure the scan tool has enough power. Use a battery charger or power supply if needed.
- Check Vehicle Compatibility: Verify that your scan tool and software are compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
Handling Software Errors
Software errors can stop the programming process. These errors can occur if there is a problem with the software file, the scan tool, or the TCM itself. This section explains how to identify and address common software errors. It gives you methods to make sure the software is correctly installed and that the programming process goes smoothly. By learning these steps, you will be prepared to fix problems quickly. This will reduce downtime and make sure your transmission works right.
- Verify Software Compatibility: Make sure the software is compatible with your scan tool and your vehicle.
- Check Software Integrity: Before programming, check the software file for corruption. Re-download the software file if necessary.
- Update Firmware: Make sure your scan tool’s firmware is up to date. This often fixes compatibility issues.
- Restore to Factory Settings: If possible, restore the TCM to its original settings. This might fix issues caused by corrupted software.
Dealing with TCM Failures
In rare instances, the TCM itself might fail during the programming process. This can happen due to power surges, software errors, or other internal problems. This section details what to do when a TCM fails. It includes steps for diagnosing the problem, replacing the TCM, and restoring the vehicle to working order. Being prepared for these situations can help minimize downtime and repair costs.
- Diagnosis: Use your scan tool to check for communication errors. This could indicate a TCM failure.
- Power Cycle: Disconnect the battery and let the vehicle sit for a few minutes. Then reconnect the battery.
- Re-Programming the New TCM: Once the new TCM is installed, reprogram it with the correct software.

Frequently Asked Questions
Question: Can I program the TCM myself at home?
Answer: Yes, you can program the TCM at home. You need a suitable scan tool and the right software. Always follow the instructions very carefully. If you are uncertain about any step, it’s best to seek help from a professional.
Question: What is the main thing that can go wrong when programming the TCM?
Answer: One of the most common issues is a loss of power during the programming process. To avoid this, make sure your car battery is in good condition, or use a battery charger or power supply to maintain a stable voltage.
Question: Where can I get the software I need?
Answer: You can obtain the software from the vehicle manufacturer, or through aftermarket software providers. Be sure to select the correct software for your car’s make, model, and year.
Question: How long does the TCM programming process usually take?
Answer: The programming process can take anywhere from 15 minutes to an hour, or sometimes even longer. This depends on the specific vehicle and the type of programming being done.
Question: What do I do if something goes wrong during the programming process?
Answer: If a problem occurs, do not panic. Try to restore the original settings or consult the scan tool’s error messages. If you are having trouble, call a professional or seek advice from automotive forums or experts.
Final Thoughts
Now that you’ve explored How to Program a Transmission Control Module Correctly, you should have a solid foundation to start your process. From gathering the right tools to working through potential problems, you have all of the steps you need. Remember, patience and proper preparation are key. Make sure to back up your data, follow instructions, and double-check your work at every stage. Don’t be afraid to ask for help if you need it. By using this guide and following the steps closely, you can get reliable results. With the right approach and a steady hand, you can confidently program a TCM and enjoy the benefits of a well-functioning transmission.

